Whenever we define FOREIGN KEY with CASCADE options for UPDATE/DELETE in more than one column on a table the following error occurred.
Scenario:
1. I have one Parent table named "Table1"
IF OBJECT_ID('Table1','U') IS NULL
Create Table Table1
(
Id INT IDENTITY(1,1) PRIMARY KEY,
Column1 VARCHAR(10)
)
GO
2. I have one child table named "Table2"
IF OBJECT_ID('Table2','U') IS NULL
Create Table Table2
(
Id INT,
Column2 VARCHAR(10),
Id_2 INT
)
GO
3. Defining FOREIGN KEY with CASCADE option and reproducing the Error:
I just want to define FOREIGN KEY on Id and Id_2 columns with CASCADE option.
The following script will work fine
ALTER TABLE dbo.TABLE2
ADD CONSTRAINT Fk_Id FOREIGN KEY(Id)
REFERENCES dbo.Table1(Id) ON UPDATE CASCADE
GO
Command(s) completed successfully.
The following script fails with Error, This table already used the Key column "Table1(Id)" with CASCADE Option..
ALTER TABLE dbo.TABLE2
ADD CONSTRAINT Fk_Id_2 FOREIGN KEY(Id_2)
REFERENCES dbo.Table1(Id) ON UPDATE CASCADE
GO
Msg 1785, Level 16, State 0, Line 1
Introducing FOREIGN KEY constraint 'Fk_Id_2' on table 'Table2' may cause cycles or multiple cascade paths. Specify ON DELETE NO ACTION or ON UPDATE NO ACTION, or modify other FOREIGN KEY constraints.
Msg 1750, Level 16, State 0, Line 1
Could not create constraint. See previous errors.
Reason:
- The Key column "Table1(Id)" have been referred on "Table2(Id) and Table2(Id_2)" columns, So it throwing an Error.
- In such scenario, we can go for Trigger
Remote table-valued function calls are not allowed.
Normally, when we access any objects(Table, View....) from Remote server using Four part naming convension through Linked Server as given below...
Select Column1, Column2 From Server2.Database1.Dbo.Table1(NOLOCK)
The following Error occurred...
Remote table-valued function calls are not allowed.
Solution:
Select Column1, Column2 From Server2.Database1.Dbo.Table1 WITH(NOLOCK) instead of NOLOCK
This error will not occur, When we access the Objects from different database or same database within the same instance or server. But, when we go to different Instance or server, NOLOCK should be used along with WITH keyword(i.e: WITH(NOLOCK)) instead of NOLOCK
Select Column1, Column2 From Server2.Database1.Dbo.Table1(NOLOCK)
The following Error occurred...
Remote table-valued function calls are not allowed.
Solution:
Select Column1, Column2 From Server2.Database1.Dbo.Table1 WITH(NOLOCK) instead of NOLOCK
This error will not occur, When we access the Objects from different database or same database within the same instance or server. But, when we go to different Instance or server, NOLOCK should be used along with WITH keyword(i.e: WITH(NOLOCK)) instead of NOLOCK
Number of referencing columns in foreign key differs from number of referenced columns, table 'TableName'.
When creating/adding referential integrity constraints on a Table, The following error occurred in various scenarios as given below..
Number of referencing columns in foreign key differs from number of referenced columns, table 'TableName'.
Meaning:
Column name not specified for the foreign key constraints.
When creating table:
IF OBJECT_ID('Tb_Table2','U') IS NULL
CREATE TABLE Tb_Table2
(
Id INT,
Column2 VARCHAR(10),
CONSTRAINT FK_ID FOREIGN KEY REFERENCES Tb_Table1(Id)
)
GO
or
Adding foreign key constraint on existing table:
ALTER TABLE Tb_Table2 ADD CONSTRAINT FK_ID FOREIGN KEY REFERENCES Tb_Table1(Id)
GO
Column name not specified for Foreign key constraints in both scripts
The script should be as follows...
IF OBJECT_ID('Tb_Table2','U') IS NULL
CREATE TABLE Tb_Table2
(
Id INT,
Column2 VARCHAR(10),
CONSTRAINT FK_ID FOREIGN KEY(Id) REFERENCES Tb_Table1(Id)
)
GO
or
ALTER TABLE Tb_Table2 ADD CONSTRAINT FK_ID FOREIGN KEY(Id) REFERENCES Tb_Table1(Id)
GO
Here, Id is the Parent table Key column.
Number of referencing columns in foreign key differs from number of referenced columns, table 'TableName'.
Meaning:
Column name not specified for the foreign key constraints.
When creating table:
IF OBJECT_ID('Tb_Table2','U') IS NULL
CREATE TABLE Tb_Table2
(
Id INT,
Column2 VARCHAR(10),
CONSTRAINT FK_ID FOREIGN KEY REFERENCES Tb_Table1(Id)
)
GO
or
Adding foreign key constraint on existing table:
ALTER TABLE Tb_Table2 ADD CONSTRAINT FK_ID FOREIGN KEY REFERENCES Tb_Table1(Id)
GO
Column name not specified for Foreign key constraints in both scripts
The script should be as follows...
IF OBJECT_ID('Tb_Table2','U') IS NULL
CREATE TABLE Tb_Table2
(
Id INT,
Column2 VARCHAR(10),
CONSTRAINT FK_ID FOREIGN KEY(Id) REFERENCES Tb_Table1(Id)
)
GO
or
ALTER TABLE Tb_Table2 ADD CONSTRAINT FK_ID FOREIGN KEY(Id) REFERENCES Tb_Table1(Id)
GO
Here, Id is the Parent table Key column.
Table level constraint does not specify column list, table 'TableName'.
When creating Primary Key or Foreign Key like constraint, The following error occurred..
Table level constraint does not specify column list, table 'TableName'.
Meaning:
Column Name or Column List not specified for the constraints.
When creating Table:
IF OBJECT_ID('Tb_Table1','U') IS NULL
CREATE TABLE Tb_Table1
(
Id INT IDENTITY(1,1),
Column1 VARCHAR(10),
CONSTRAINT PK_Id PRIMARY KEY
)
or
When adding constraint on existing table:
ALTER TABLE Tb_Table1 ADD CONSTRAINT PK_Id PRIMARY KEY
GO
The error occurred, Here No column or Column list specified..
The script should be as follows...
IF OBJECT_ID('Tb_Table1','U') IS NULL
CREATE TABLE Tb_Table1
(
Id INT IDENTITY(1,1),
Column1 VARCHAR(10),
CONSTRAINT PK_Id PRIMARY KEY(Id)
)
or
ALTER TABLE Tb_Table1 ADD CONSTRAINT PK_Id PRIMARY KEY (Id)
GO
Table level constraint does not specify column list, table 'TableName'.
Meaning:
Column Name or Column List not specified for the constraints.
When creating Table:
IF OBJECT_ID('Tb_Table1','U') IS NULL
CREATE TABLE Tb_Table1
(
Id INT IDENTITY(1,1),
Column1 VARCHAR(10),
CONSTRAINT PK_Id PRIMARY KEY
)
or
When adding constraint on existing table:
ALTER TABLE Tb_Table1 ADD CONSTRAINT PK_Id PRIMARY KEY
GO
The error occurred, Here No column or Column list specified..
The script should be as follows...
IF OBJECT_ID('Tb_Table1','U') IS NULL
CREATE TABLE Tb_Table1
(
Id INT IDENTITY(1,1),
Column1 VARCHAR(10),
CONSTRAINT PK_Id PRIMARY KEY(Id)
)
or
ALTER TABLE Tb_Table1 ADD CONSTRAINT PK_Id PRIMARY KEY (Id)
GO
How to Restore MASTER database...
Why/when should restore the Master database:
- Incase of any failure login into an Instance due to forgot the login credentials
- Windows authentication credentials removed mistakenly and Sysadmin('sa') password also changed...
- we can fix this issue by restoring the Master database.
When should backup the Master database ?
1. If any changes done at Master database like whenever new login created/modified
2. New database created or Mapped the user with database.
What are the things needs to be considered before restore the Master database ?
1. If there is any changes to Master database after the database backup created.
2. Any login created/modified after the Master database backup created.
3. Any associated/mapped user with user databases after the Master database backup created.
4. Any user database created after the Master database backup created.
5. Any user database re-attached as it creates system tables to maintain the availability.
6. Any objects, logins, or databases have been deleted after Master database was backed up, those objects, logins, and databases should be deleted from Master database also.
7. Any user database no longer available that are referenced in a Master database backup, It report errors when restoring the Master database. Those databases should be dropped after the Master backup is restored.
8. The SQL Server instance stopped automatically once the Master database restore activity completed.
How to restore the Master database backup ?
Restoring Master database is not direct way like user defined database as it needs some additional workarround here..
1. Identify the Sqlservr.exe location.
2. Stop the SQL Server Instance.
3. Start the SQL Server in single user mode from command prompt...
If the SQL Server is Default instance:
If the SQL Server is Named instance:
Press Enter to proceed...
Once the system databases started as shown below... "Please don't close this screen"
4. Open the "SQL Server Management studio" from Start --> Program Files --> ...
5. Login into the Instance with Windows Authentication, The Instance doesn't have windows authentication credential, But we can login through Single user mode...
6. Expand the System Databases --> Right click on Master Database --> Tasks --> Restore --> Database... as shown below
7. Enter as Master in To Database area, Locate the Master database backup file with REPLACE Mode.
8. It may receive any error stating that "Single session is already running..." (or) "A transport-level error has occurred when receiving results from the server", Just click OK and Cancel to proceed further...
9. Now the command prompt can be closed once the restore process completed...
10. Start the SQL Server Instance service.
11. Open the "SQL Server Management studio" from Start --> Program Files --> ...
- Incase of any failure login into an Instance due to forgot the login credentials
- Windows authentication credentials removed mistakenly and Sysadmin('sa') password also changed...
- we can fix this issue by restoring the Master database.
When should backup the Master database ?
1. If any changes done at Master database like whenever new login created/modified
2. New database created or Mapped the user with database.
What are the things needs to be considered before restore the Master database ?
1. If there is any changes to Master database after the database backup created.
2. Any login created/modified after the Master database backup created.
3. Any associated/mapped user with user databases after the Master database backup created.
4. Any user database created after the Master database backup created.
5. Any user database re-attached as it creates system tables to maintain the availability.
6. Any objects, logins, or databases have been deleted after Master database was backed up, those objects, logins, and databases should be deleted from Master database also.
7. Any user database no longer available that are referenced in a Master database backup, It report errors when restoring the Master database. Those databases should be dropped after the Master backup is restored.
8. The SQL Server instance stopped automatically once the Master database restore activity completed.
How to restore the Master database backup ?
Restoring Master database is not direct way like user defined database as it needs some additional workarround here..
1. Identify the Sqlservr.exe location.
2. Stop the SQL Server Instance.
3. Start the SQL Server in single user mode from command prompt...
If the SQL Server is Default instance:
If the SQL Server is Named instance:
Press Enter to proceed...
Once the system databases started as shown below... "Please don't close this screen"
4. Open the "SQL Server Management studio" from Start --> Program Files --> ...
5. Login into the Instance with Windows Authentication, The Instance doesn't have windows authentication credential, But we can login through Single user mode...
6. Expand the System Databases --> Right click on Master Database --> Tasks --> Restore --> Database... as shown below
7. Enter as Master in To Database area, Locate the Master database backup file with REPLACE Mode.
8. It may receive any error stating that "Single session is already running..." (or) "A transport-level error has occurred when receiving results from the server", Just click OK and Cancel to proceed further...
9. Now the command prompt can be closed once the restore process completed...
10. Start the SQL Server Instance service.
11. Open the "SQL Server Management studio" from Start --> Program Files --> ...
Why SPARSE column ?
Sparse Column:
Sparse column is like a normal column that has optimized storage for NULL.
Sparse column reduces the space requirement for NULL.
If the column value is NULL then, the values require NO STORAGE.
Using Normal Column:
IF OBJECT_ID('Tb_NormalColumn','U') IS NOT NULL
DROP TABLE Tb_NormalColumn
GO
CREATE TABLE Tb_NormalColumn
(
ID INT IDENTITY(1,1),
Column1 VARCHAR(100) NULL,
Column2 VARCHAR(100) NULL
)
GO
INSERT Tb_NormalColumn(Column2) VALUES('www.sqlserverbuddy.blogspot.com')
GO 1000
Here, The column1 uses NULL and It consumes some spaces in allocation.
sp_spaceused Tb_NormalColumn
GO
Using SPARSE Column:
IF OBJECT_ID('Tb_SparseColumn','U') IS NOT NULL
DROP TABLE Tb_SparseColumn
GO
CREATE TABLE Tb_SparseColumn
(
ID INT IDENTITY(1,1),
Column1 VARCHAR(100) SPARSE NULL,
Column2 VARCHAR(100) NULL
)
GO
INSERT Tb_SparseColumn(Column2) VALUES('www.sqlserverbuddy.blogspot.com')
GO 1000
Here, The column1 uses NULL and It consumes some spaces in allocation.
sp_spaceused Tb_SparseColumn
GO
To identity the SPARSE column:
SELECT name,is_sparse FROM sys.columns WHERE [object_id] = object_id('Tb_SparseColumn')
GO
Limitation of using SPARSE column:
1. SPARSE column should be Nullable.
2. It can not have RowGuidCol or Identity property and Filestream attribute.
3. It can not be Text, nText, Image, Timestamp, Geometry, Geography & User defined data type.
4. It can not have Default value, Computed columns.
5. It can not be a part of Clustered Index or Primary Key.
6. Normally, a row can have maximum of 8060 bytes. But, when using SPARSE column, row size will be 8018 bytes only.
7. When changing a normal column to a SPARSE column, the SPARSE column will consume more space for nonnull values than the normal columns.
Note: This feature NOT available prior to SQL Server 2008.
Conclusion:
Using SPARSE column, we can avoide/reduce memory allocation for NULL values
Rows are not deleted from the tables named in the FROM clause...
The question is "Rows are not deleted from the tables named in the FROM clause of the DELETE statement" ?
The answer is Yes and No
NO ?
Normally, when we use DELETE statement on Independent table, The records will be deleted from the tables named in the FROM clause.
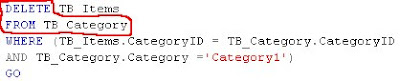
DELETE FROM TB_Items WHERE CategoryID = 1
But, we can also use the script without FROM clause here...
YES ?
when we use DELETE statement on dependent table, The records has to be deleted from the table1 which dependent on table2.
Basically, when we perform a DELETE operation on a table, The records will be removed from the table named in "FROM CLAUSE as given below".
But, What the image shows below is "Different"
When we perform DELETE operation on a table which is based on some other table then, The record will be removed from the table named nearby the DELETE statement, Not from the "FROM CLAUSE".
The answer is Yes and No
NO ?
Normally, when we use DELETE statement on Independent table, The records will be deleted from the tables named in the FROM clause.
DELETE FROM TB_Items WHERE CategoryID = 1
But, we can also use the script without FROM clause here...
YES ?
when we use DELETE statement on dependent table, The records has to be deleted from the table1 which dependent on table2.
Basically, when we perform a DELETE operation on a table, The records will be removed from the table named in "FROM CLAUSE as given below".
But, What the image shows below is "Different"
When we perform DELETE operation on a table which is based on some other table then, The record will be removed from the table named nearby the DELETE statement, Not from the "FROM CLAUSE".
Alternate to DBCC CLEANTABLE
Normally, we will execute this whenever we do some significant changes to variable-length columns in a table or indexed view.
But, we can also do some alternate to this activity.
Yes
we can Rebuild the indexes on tables and viewes.
But, we can also do some alternate to this activity.
Yes
we can Rebuild the indexes on tables and viewes.
Backup and restore operations are not allowed on database tempdb
1.Tempdb is re-created every time SQL Server is started so that the system always starts with a clean copy of the database.
2.Temporary tables and stored procedures are dropped automatically on disconnect.
So, Backup and restore operations are not allowed on tempdb
2.Temporary tables and stored procedures are dropped automatically on disconnect.
So, Backup and restore operations are not allowed on tempdb
Failed to update database "DATABASE" because the database is read-only.
The reasone may be any one of the following
1. The database is Read-Only (or)
2. The database is a Snapshot
How to identity whether the database is Read-Only, Snapshot and Source database of the snapshot ?
a) Read-Only:
SELECT DATABASEPROPERTYEX('DatabaseName','Updateability') 'Read Only'
Read Only
READ_ONLY
SELECT Is_Read_Only 'Read Only' FROM SYS.databases WHERE name = 'DatabaseName'
Read Only
1
b) Snapshot source:
SELECT CASE WHEN DB_NAME(source_database_id) IS NULL THEN 'Not a Snapshot' ELSE 'Snapshot Created from ' + '"' + DB_NAME(source_database_id) + '"' END 'Source DB Name' FROM SYS.databases
WHERE name = 'DatabaseName'
If the Database is not a Snapshot
Source DB Name
Not a Snapshot
If the Database is a Snapshot
Source DB Name
Snapshot Created from "SourceDatabaseName"
Note: Snapshot can not be created for Log file:
Log files, offline files, restoring files, and defunct files for database snapshots should not be specified. "Database_log" is not an eligible file for a database snapshot.
1. The database is Read-Only (or)
2. The database is a Snapshot
How to identity whether the database is Read-Only, Snapshot and Source database of the snapshot ?
a) Read-Only:
SELECT DATABASEPROPERTYEX('DatabaseName','Updateability') 'Read Only'
Read Only
READ_ONLY
SELECT Is_Read_Only 'Read Only' FROM SYS.databases WHERE name = 'DatabaseName'
Read Only
1
b) Snapshot source:
SELECT CASE WHEN DB_NAME(source_database_id) IS NULL THEN 'Not a Snapshot' ELSE 'Snapshot Created from ' + '"' + DB_NAME(source_database_id) + '"' END 'Source DB Name' FROM SYS.databases
WHERE name = 'DatabaseName'
If the Database is not a Snapshot
Source DB Name
Not a Snapshot
If the Database is a Snapshot
Source DB Name
Snapshot Created from "SourceDatabaseName"
Note: Snapshot can not be created for Log file:
Log files, offline files, restoring files, and defunct files for database snapshots should not be specified. "Database_log" is not an eligible file for a database snapshot.
The log or differential backup cannot be restored because no files are ready to rollforward.
All restore operations start with the restore of a FULL backup. It isn’t possible to restore only a Differential or a Log backup.
Both need a reference of the LSN(Log Sequence Number) to proceed.
When we try to restore Differential or Log backup directly without any Full backup, The following Err occurred... Because the differential or log backup will not have LSN to continue.
"The log or differential backup cannot be restored because no files are ready to rollforward."
To identify/verify whether the backup file (LSN) sequence is valid or not
SELECT Name,first_lsn,last_lsn,checkpoint_lsn,database_backup_lsn FROM msdb..backupset WHERE database_name = 'PandianDB' ORDER BY backup_start_date, media_set_id
1. Differential backup Database_Backup_LSN should match with Full Backup Checkpoint_LSN
2. Log backup Database_Backup_LSN should match with Differential Backup Checkpoint_LSN
3. Some times Differential backup and Log backup Checkpoint_LSN are the same. The meaning is "There is no any write operation performed after the Differential backup taken"
Both need a reference of the LSN(Log Sequence Number) to proceed.
When we try to restore Differential or Log backup directly without any Full backup, The following Err occurred... Because the differential or log backup will not have LSN to continue.
"The log or differential backup cannot be restored because no files are ready to rollforward."
To identify/verify whether the backup file (LSN) sequence is valid or not
SELECT Name,first_lsn,last_lsn,checkpoint_lsn,database_backup_lsn FROM msdb..backupset WHERE database_name = 'PandianDB' ORDER BY backup_start_date, media_set_id
1. Differential backup Database_Backup_LSN should match with Full Backup Checkpoint_LSN
2. Log backup Database_Backup_LSN should match with Differential Backup Checkpoint_LSN
3. Some times Differential backup and Log backup Checkpoint_LSN are the same. The meaning is "There is no any write operation performed after the Differential backup taken"
How to force Checkpoint process to occur every 2 minutes
Normally, The recovery interval is default to 0. It means SQL Server dynamically manages how offen a checkpoint occure.
We can force the SQL Server to occur the recovery interval every 2 minutes
sp_configure 'Show Advanced Options',1
GO
sp_configure 'Recovery Interval',2
Reconfigure with Override
GO
sp_configure 'Show Advanced Options',0
GO
To identify Clustered and Non-Clustered Primary key table(s) in the Database ?
To fetch all the Primary key tables in the current Database.
Use SQLServerBuddy
Go
SELECT
O.[NAME] 'Table Name',
I.[NAME] 'Key Name',
CASE I.[TYPE] WHEN 2 THEN 'Non Clustered Primary Key' ELSE 'Clustered Primary Key' END 'Clustered /NonClustered'
FROM SYS.INDEXES I JOIN SYS.OBJECTS O
ON (I.[OBJECT_ID] = O.[OBJECT_ID])
WHERE O.[TYPE] = 'U'
AND I.IS_PRIMARY_KEY = 1
ORDER BY 1
The column Type in Sys.Indexes DMV have the following values
0 - HEAP
1 - CLUSTERED
2 - NONCLUSTERED
Use SQLServerBuddy
Go
SELECT
O.[NAME] 'Table Name',
I.[NAME] 'Key Name',
CASE I.[TYPE] WHEN 2 THEN 'Non Clustered Primary Key' ELSE 'Clustered Primary Key' END 'Clustered /NonClustered'
FROM SYS.INDEXES I JOIN SYS.OBJECTS O
ON (I.[OBJECT_ID] = O.[OBJECT_ID])
WHERE O.[TYPE] = 'U'
AND I.IS_PRIMARY_KEY = 1
ORDER BY 1
The column Type in Sys.Indexes DMV have the following values
0 - HEAP
1 - CLUSTERED
2 - NONCLUSTERED
A particular stored procedure used in which JOB
Here, we want to search a particular stored procedure(USP_Proc1) used in wich JOB.
Use Master
Go
SELECT V.name 'JOB Name' FROM msdb.dbo.sysjobsteps s JOIN msdb.dbo.sysjobs_view v
ON(S.job_id = V.job_id)
WHERE S.command LIKE '%USP_Proc1%'
Use Master
Go
SELECT V.name 'JOB Name' FROM msdb.dbo.sysjobsteps s JOIN msdb.dbo.sysjobs_view v
ON(S.job_id = V.job_id)
WHERE S.command LIKE '%USP_Proc1%'
Scheduled JOBs in current instance
We can listout what are all the JOBs scheduled in our Instance.
1. To listout scheduled jobs in current instance:
USE master
Go
EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_help_job
(or)
SELECT * FROM msdb.dbo.sysjobs_view
2. To listout particular JOB's Steps, Schedules,...Etc
DECLARE @JOBID UNIQUEIDENTIFIER
SELECT @JOBID = job_id FROM msdb.dbo.sysjobs_view
WHERE name = 'JOB Name'
EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_help_jobstep @job_id=@JOBID
EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_help_jobschedule @job_id=@JOBID
1. To listout scheduled jobs in current instance:
USE master
Go
EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_help_job
(or)
SELECT * FROM msdb.dbo.sysjobs_view
2. To listout particular JOB's Steps, Schedules,...Etc
DECLARE @JOBID UNIQUEIDENTIFIER
SELECT @JOBID = job_id FROM msdb.dbo.sysjobs_view
WHERE name = 'JOB Name'
EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_help_jobstep @job_id=@JOBID
EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_help_jobschedule @job_id=@JOBID
The SELECT permission was denied on the object 'sys...', database 'msdb', schema 'dbo'.
When we try to access the SQL Server Agent related system tables, The following Error occurred
Msg 229, Level 14, State 5, Line 1
The SELECT permission was denied on the object 'sys...', database 'msdb', schema 'dbo'.
What are the Database role needed to access the following SQL Server Agent system tables ?
USE MSDB
Go
The following system tables needed SQLAgentOperatorRole database role
sysalerts,
sysnotifications,
sysoperators
The following system table needed SQLAgentUserRole database role
syscategories
The following system tables needed TargetServersRole database role
sysdownloadlist,
sysjobs,
sysjobservers,
systargetservers,
syssubsystems
The following system tables needed db_Owner database role
sysjobactivity,
sysjobhistory,
sysjobschedules,
sysjobsteps,
sysjobstepslogs,
systargetservergroupmembers,
systargetservergroups,
systaskids,
sysproxies,
sysproxylogin,
sysproxysubsystem,
sysschedules,
syssessions
Granting Database Role to a Login:
USE msdb
GO
EXEC sp_addrolemember N'RoleName', N'Login'
Msg 229, Level 14, State 5, Line 1
The SELECT permission was denied on the object 'sys...', database 'msdb', schema 'dbo'.
What are the Database role needed to access the following SQL Server Agent system tables ?
USE MSDB
Go
The following system tables needed SQLAgentOperatorRole database role
sysalerts,
sysnotifications,
sysoperators
The following system table needed SQLAgentUserRole database role
syscategories
The following system tables needed TargetServersRole database role
sysdownloadlist,
sysjobs,
sysjobservers,
systargetservers,
syssubsystems
The following system tables needed db_Owner database role
sysjobactivity,
sysjobhistory,
sysjobschedules,
sysjobsteps,
sysjobstepslogs,
systargetservergroupmembers,
systargetservergroups,
systaskids,
sysproxies,
sysproxylogin,
sysproxysubsystem,
sysschedules,
syssessions
Granting Database Role to a Login:
USE msdb
GO
EXEC sp_addrolemember N'RoleName', N'Login'
The user does not have permission to perform this action.
Scenario:
We have created a new Login (ie: Test) and Login into this account and able to access the Databases.
When I try to execute DMVs like SYS.dm_exec_connections, The following Err occurred.
Msg 297, Level 16, State 1, Line 1
The user does not have permission to perform this action.
So, The login required some Server permission to access the DMVs. correct ?
Login into sa account and grant the following permission to login: test
USE master
GO
GRANT VIEW SERVER STATE TO [test]
The View Server State permission granted to the Test Login.
Now we can access the DMVs.
We have created a new Login (ie: Test) and Login into this account and able to access the Databases.
When I try to execute DMVs like SYS.dm_exec_connections, The following Err occurred.
Msg 297, Level 16, State 1, Line 1
The user does not have permission to perform this action.
So, The login required some Server permission to access the DMVs. correct ?
Login into sa account and grant the following permission to login: test
USE master
GO
GRANT VIEW SERVER STATE TO [test]
The View Server State permission granted to the Test Login.
Now we can access the DMVs.
Migrating MS Access 2003 Database to SQL Server 2008
What is Migration ? Migrating from one Product type to another Product type.
ie: MSAccess to SQL Server, Oracle to SQL Server
What is Upgradation ?
Upgrading from one Edition/Version to another Edition/Version within the same Product type.
ie: SQL Server 2005 to SQL Server 2008
Here, we going to Migrate Microsoft Access 2003 Database to SQL Server 2008.
http://www.microsoft.com/sqlserver/2008/en/us/migration.aspx
2. Once launched the page, Click the appropriate link as given below
3. Once click the link, Download page will appear and Click Download Button. Once download completed.
4. Double click the downloaded file.
9. Follow the screen as given below
10. Click Next button and follow the screen sequence.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
21.Licence Management required to login MSN Live ID
23.
24.
25.
26.
27.
28.
29.
30.
31.If we want to retain the link between MSAccess Database and SQL Server, Just Check the Link Tables check box, If you don't want to link the tables, Just uncheck.
32.
33.
34.
35.
36.
37.


Microsoft Access 2003 database successfully migrated to SQL Server 2008.
ie: MSAccess to SQL Server, Oracle to SQL Server
What is Upgradation ?
Upgrading from one Edition/Version to another Edition/Version within the same Product type.
ie: SQL Server 2005 to SQL Server 2008
Here, we going to Migrate Microsoft Access 2003 Database to SQL Server 2008.
1. We have SSMA (SQL Server Migration Assistant) tool which can be downloaded from the url given below
http://www.microsoft.com/sqlserver/2008/en/us/migration.aspx
2. Once launched the page, Click the appropriate link as given below
3. Once click the link, Download page will appear and Click Download Button. Once download completed.
4. Double click the downloaded file.
5. Follow the screens as given below
6. Click Next.
7. Click Download Button.
8. Once downloaded the OLEDB provider for MSAccess, Double click the .exe file.
9. Follow the screen as given below
10. Click Next button and follow the screen sequence.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.Licence Management required to login MSN Live ID
23.
24.
25.
26.
27.
28.
29.
30.
31.If we want to retain the link between MSAccess Database and SQL Server, Just Check the Link Tables check box, If you don't want to link the tables, Just uncheck.
32.
33.
34.
35.
36.
37.

Microsoft Access 2003 database successfully migrated to SQL Server 2008.
Upgrade SQL 2005 to SQL 2008
Here, I am going to upgrade SQL Server 2005 Standard Edition to SQL Server 2008 Standard Edition.
What are the Version and Edition supports when upgrade - Go to Bottom of this post.
SQL Server Upgrade Advisor helps us prepare for upgrades to SQL Server 2008. Upgrade Advisor analyzes installed components from earlier versions of SQL Server, and then generates a report that identifies issues to fix either before or after we upgrade.
1. Take a Backup of System Databases and User Defined Databases.
2. Generate Scripts for Replications, Right Click on Replication --> Generate Scripts
3. Make a list of Linked Servers on the Existing SQL Servers.
4. Start the SQL Server, SQL Server Agent, SQL Server Analysis Services, SQL Server Full Text Search, SQL Server Reporting Services which you going to Upgrade(SQL Server 2005)
5. Step Into SQL Server 2008 Setup --> Setup.exe -->
6. Now you will have SQL Server Installation Center screen as given below
7. Click the Install Upgrade Advisor, So we can easily identify what are all the prerequisites, Warnings and Errors.
8. Once you completed the Installation of Upgrade Advisor.
9. Click the SQL Server 2008 Upgrade Advisor as given above.
10. It will open a window named Microsoft SQL Server 2008 Upgrade Advisor and Click the link as given below
11. It will open a wizard and click Next as given below
12. SQL Server components window shows that what the components to be upgraded. In this case we could not select Notification Services. Because, Notification Service is deprecated in SQL Server 2008. So Un-check the checkbox for Notification Services.
13. Just Click the Detect button to fetch the Server name. (So, we can select which Server want to Upgrade)
14. Click the Next Button as given above.
15. It will show Connection Parameters wizard, In that wizard, Select the Instance Name which you want to Upgrade and Provide the Authentication and Credentials as given below.
16. Select the button next. SQL Server Parameters wizard appears, in that wizard, select the all Databases which you want to analyze as given below.
17. Click the Button Next.
18. It will prompt Reporting Service Instance and Analysis Service Instance; select the Instance name for each.
19. It will prompt DTS Parameters. Just select and Click Next button
20. Click the option for SSIS Parameters. Just select and Click Next button.
21. Click the Run button on Confirm Upgrade Advisor Settings wizard.
22. Once the analysis completed. It shows the Analysis status wizard as given below.
23. Once completed the analysis. Click the Launch Report button.
24. In this wizard, Select which service you want to see the Errors / Warnings as given below.
25. Once the Warnings / Errors fixed, Click the Back button and Click the Run button until the all services success.
26. Once the Upgrade Advisor completed successfully.
27. Run the Setup.exe file.
28. Click the link Upgrade from SQL Server 2000 or SQL Server 2005 under Installation as given below
29. The Upgrade process started.
30. It passes the all Setup support rules.
31. Click the OK button
32. Click Install button.
33. Click the Next button as given below
34. Enter the Product Key and Click Next Button.
35. Select the I accept the license terms check box and Click Next button
36. It will browse the all available instances on the server, Select the Instance to upgrade as given below
37. Click the Next button on Select Instance wizard.
38. Click the Next button on Select Features wizard.
39. Click the Next button on Instance Configuration wizard.
40. Click the Next button on Disk Space Requirements wizard.
41. Click the Next button on Server Configuration wizard.
42. Click the Next button on Full-text Upgrade wizard.
43. Click the Next button on Reporting Services Authentication (Windows / Mixed Mode) wizard.
44. Click the Next button on Error and Usage Reporting wizard.
45. If the Up gradation Rule is not matching with the Edition and Version then, It will show an Error as given below
46. Otherwise, Click the Next button on Upgrade Rules wizard.
47. Ready to Upgrade wizard appears as given below
48. Click the Button Upgrade on Ready to upgrade wizard.
49. Once the Upgrade Process completed, Click the Next button as given below
50. Once the Complete process completed the screen looks like as given below
51. Complete upgrade activity report available as a link on local machine.
52. When you select the Link the text file looks like as below
53. Click the Close button.
54. I try to connect the Instance SQL2005 using SQL Server 2005 Standard Edition, But It is throwing an Error as given below
55. Because, we have upgraded the SQL2005 instance to SQL Server 2008 Standard.
56. Now, I try to connect the Instance SQL2005 using SQL Server 2008 Standard Edition, I can able to connect it.
57. Finally, I examined the Upgraded server. All the Databases, Login Credentials, Linked Servers, Replications are accessible in SQL Server 2008 Standard Edition now as given below
58. The instance name is same as SQL2005, but the edition is SQL Server 2008 Standard Edition.
Version and Edition Upgrade Path
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms143393(v=SQL.100).aspx
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)